Multiple Path Search (MPS) Example
The shortest path algorithm is designed to find a single shortest path between two vertices. However, in some cases, there might be multiple shortest paths with the same length, and you might want to retrieve all of them.
Consider the following graph based on the MPS Graph example:
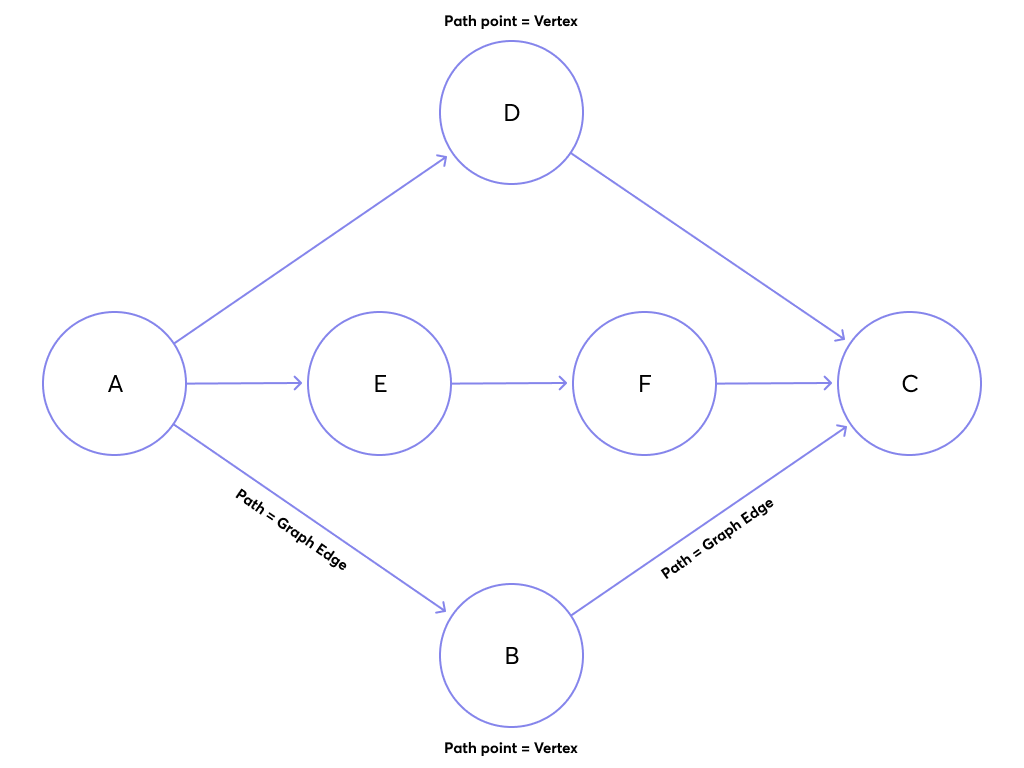
A shortest path query from A to C might return either A -> B -> C or A -> D -> C, but it's not guaranteed which one will be returned (ignoring edge weights in this example).
Finding the Shortest Path Length
You can use the following query to determine the shortest path length:
RETURN LENGTH(
FOR v IN OUTBOUND
SHORTEST_PATH "mps_verts/A" TO "mps_verts/C" mps_edges
RETURN v
)
For the example graph, the result is 3, which includes the start vertex. Subtract 1 to get the edge count or traversal depth.
Retrieving All Paths with the Shortest Length
To find all paths with the determined length, use a pattern matching traversal. Start at vertex A and filter the results to only retrieve paths that end at vertex C.
The following query returns all paths with a length of 2, starting at vertex A and ending at vertex C:
FOR v, e, p IN 2..2 OUTBOUND "mps_verts/A" mps_edges
FILTER v._id == "mps_verts/C"
RETURN CONCAT_SEPARATOR(" -> ", p.vertices[*]._key)
Result:
[
"A -> B -> C",
"A -> D -> C"
]
A traversal depth of 3..3 would return A -> E -> F -> C and 2..3 would return all three paths.
Limitations
To achieve this result, two separate queries are required:
- First, compute the shortest path length.
- Then, based on the shortest path length (minus 1), perform the pattern matching.
This is because the min and max depth parameters in the traversal query cannot be expressions. They must be known in advance, either as number literals or bind parameters.